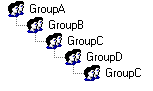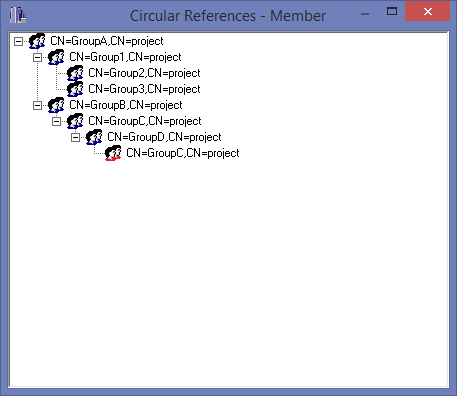
The Circular Reference features is used to determine if there are any infinite loops in the group memberships. These are examples of circular references, GroupA is a member of GroupB, and GroupB is a member of GroupA, or GroupA is a member of GroupB, GroupB is a member of GroupC and GroupC is a member of GroupA. While circular references don't really cause much of an issue for AD, it can cause issues with programs that enumerate group members and don't support nested groups. The main issues that circular reference does cause is with the resource access management and confusion on how a user received access to an item.
The feature will scan all the groups under the specified Base DN, and enumerate the membership of all the groups under the Base DN to determine if there are any circular references. The depth of the nested groups that is scanned is defined by the Depth field. By default the results will display any occurrence of a circular reference is found in the nested groups. If the Start of circular reference only option is selected, then only when the groups that are causing the circular reference will be displayed.
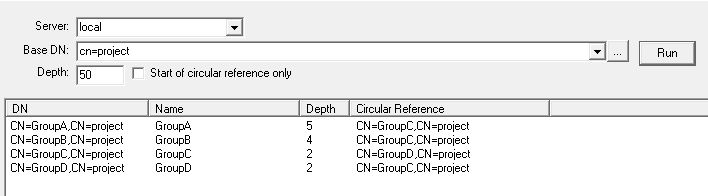
In the above example, with Start of circular reference only option is not selected then it will display all the groups that have a circular reference in the nested groups:
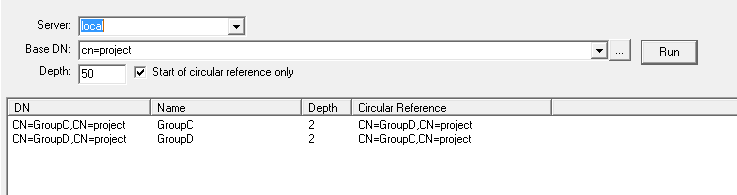
However, with the Start of circular reference only option is selected, then only the groups that cause the circular reference are returned:
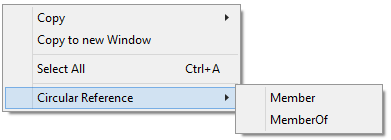
The context menu include an additional item to enable you to display the complete inheritance of the selected group, for both the member and memberof attributes.
Here is an example of group inheritance, any circular references are highlighted with a red group icon.